Although I recommend against the use of both EPA and DHA. It is interesting to find out why EPA is safer. There are multiple reasons for this, but first, let’s find out what both fats do. In short, EPA gets used up very quickly by the different cells while DHA has a longer-lasting function. That’s why most fish oil supplements put more EPA than DHA in a bottle. Furthermore, EPA can more easily be converted into DHA.
The Real Reason Why EPA Is Better
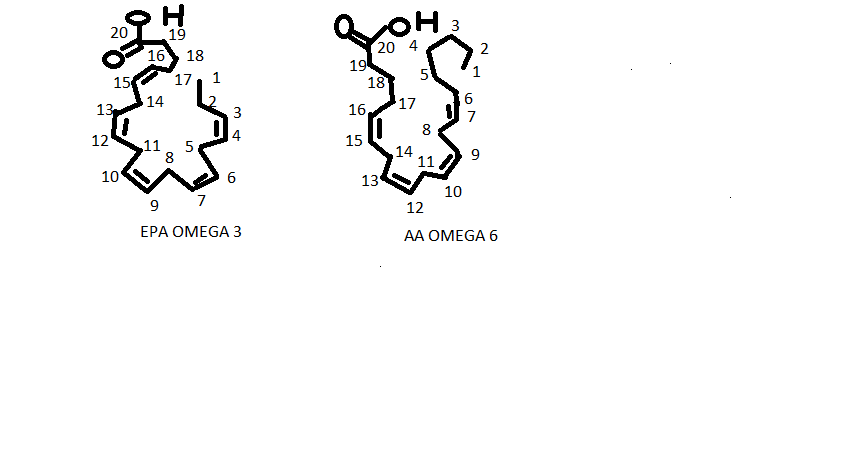
The image below is EPA (omega 3) with 20 carbons and AA (omega 6) with 20 carbons. As you can see they are quite similar. EPA is known to inhibit omega 6 (AA) from becoming a prostaglandin (PGE2). PGE2 has many different nasty side effects. Omega 3 has its own PGE3 series, but its effects are less known and researched.
Summary
- EPA has less double bonds than DHA, making EPA less fragile.
- Due to the similarity with AA, EPA can inhibit AA pathways that are known to be inflammatory, competing for the same enzymes (delta while DHA is to big (spatial size) to inhibit the omega 6 pathways into eicosanoids.
- EPA can also let AA stay in the membrane by occupying phospholipase A2. Phospholipase A2 can release AA.
Because Arachidonic Acid (AA) is so prevalent in the western diet and is beginning to be a “recognized” nutritional problem[i], stopping this fatty acid from becoming pro-inflammatory can be seen as healthy (aspirin works in the same way). Although adding DHA to an omega 6 diet, could lead to an increase in fee arachidonic acid to become active metabolites[ii]

[i] Mol Cell Biochem. 2003 Nov;253(1-2):141-9. Arachidonic acid and colorectal carcinogenesis. Jones R1, Adel-Alvarez LA, Alvarez OR, Broaddus R, Das S.
[ii] Biochim Biophys Acta. 1997 Jun 23;1346(3):305-16. Docosahexaenoic acid causes accumulation of free arachidonic acid in rat pineal gland and hippocampus to form hepoxilins from both substrates. Reynaud D1, Pace-Asciak CR.